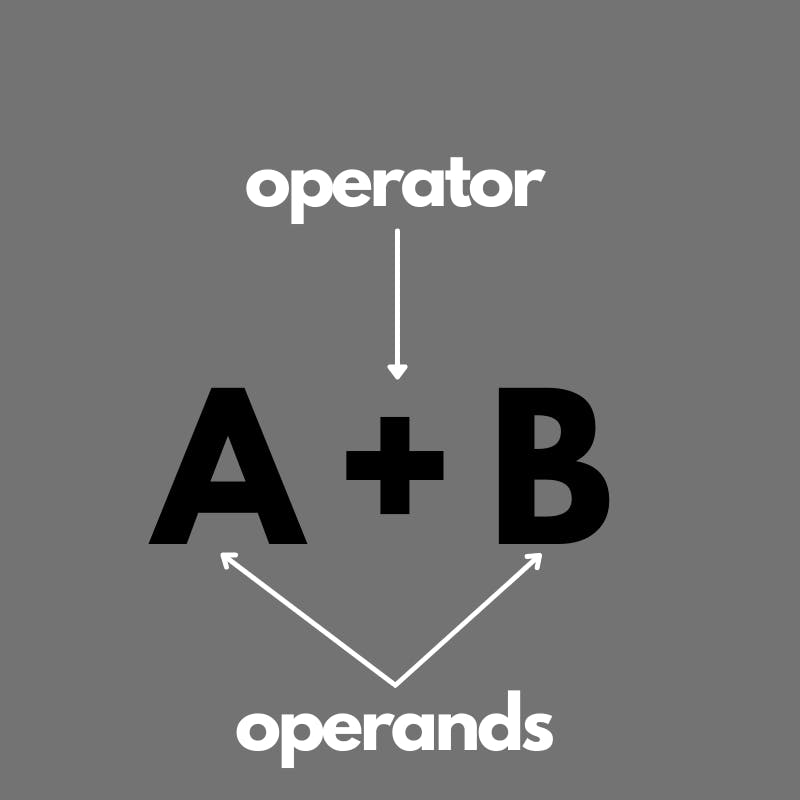
- An operator is a symbol or function denoting an operation.
Operators in programming work similar to the way they do in mathematics, for instance,
+for adding two operands or-for subtracting two operands.An operand refers to the object (e.g a number) of a mathematical operation.
In C programming there are 9 classes of operators divided as following:
i. Arithmetic Operators
- These are used to perform mathematical calculations.
+,-,*,/,%
ii. Unary Operators
- They are applied on a single operand.
-,+e.g.-1(negative 1)
++,--,sizeof (), (typecasting)
iii. Relational Operators
- These are also known as decisional operators.
<,>,<=,>=
iv. Assignment Operators
Assigns operand from the right side of the operator to the operand on the left side.
=,+=,-=,*=,/=,%=The expression
a = a/5can be written as a shortcut asa/=5.
v. Equality Operators
Checks whether two operands are equal or now.
==,!=
vi. Logical Operators
Used to evaluate two or more conditions.
&&(AND),||(OR)
vii. Conditional Operators
Also known as a ternary operators.
Used to make a decision based upon an expression.
They work similar to an if-else statement.
Uses symbols
?and:Syntax:
Condition? True statement:false statement;
- Sample code:
float money;
float cost;
money > cost? printf("You can afford it") : printf("Not Enough");
the other operators are the Bitwise Operator and Comma Operator but they are beyond the scope of this series

